What's the Difference between Beavers and Humans? – Wednesday Blog by Seán Thomas Kane
This week, to conclude a month of chaos I interviewed environmental journalist Ben Goldfarb about his book Eager: The Surprising, Secret Life of Beavers and Why They Matter.
What follows is a transcript of our conversation.
STK: This is a really fascinating book, I have to say.
STK: I was reading something back in June that was talking about the idea of the Homo faber where we should identify ourselves by our ability to build and to imagine solutions to get out of our problems. I read that and said, “that’s what beavers do to, right?” So, the premise of this one is what is the difference between humans and beavers?
STK: When you talked in the book here about the restoration of beaver dams on Bridge Creek in Oregon; could this be a model for a clearer for how humanity could adapt to cohabitate with the rest of nature?
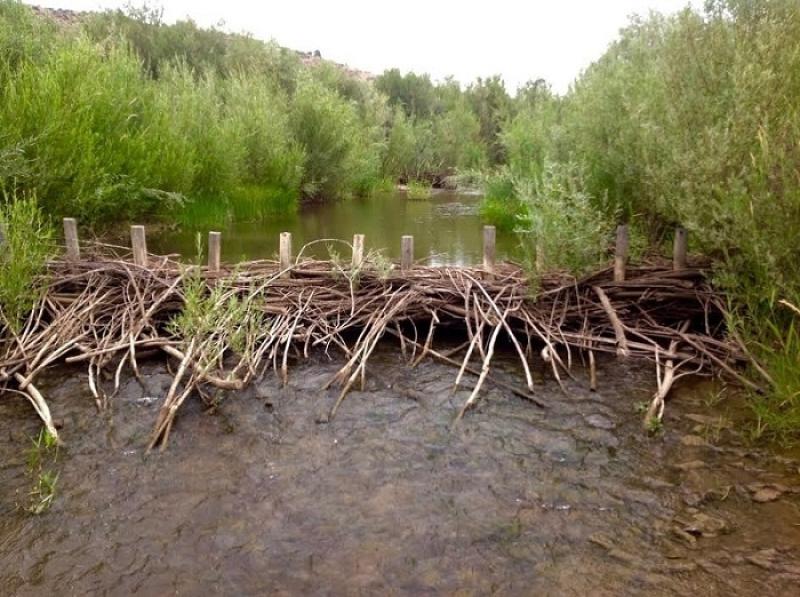
BG: Yeah, I think so. The situation in Bridge Creek and other places like that is that humans are building beaver dam analogues to help beavers flourish. When we wiped out several hundred million beavers over several centuries in North America, we made it harder for beavers to recolonize, so when you have a healthy beaver-rich stream they are pooling that water up and pushing it out onto the floodplain. When the beavers disappear there’s nothing to cool or check the water, streams then cut through the sediment on the bottom, and they turn into these miniature canyons or ravines. That’s a hard place for beavers to recolonize because the stream is trapped in its place and that’s where these human-built beaver dams come in because we can knock some big wooden posts into the stream bed and weave some willows in there and build some stability. It’s not as good as what the beavers do but it’s a starter dam that they can come in, build off of, and advance. So, these beaver dam analogues are like beaver kick starters, and they allow them to recolonize places where they otherwise couldn’t colonize. And to your point, I think we’ve spent hundreds of years in North America making life harder for beavers in many ways, mostly by killing them directly, and this is a way that we’re making life a little bit easier for them. You can apply this model onto many other wildlife restoration projects like wildlife crossings, or the planting of oyster reefs or salt marshes. These are things which work with ecosystems rather than against them.
STK: Yeah, I know they talk here about the butterfly gardens that give them a place to land and such when they migrate.
We’re the species that created the grid system whereas beavers have their own idea of fluid stability. What would you say to that?
BG: We as a species are obsessed with linearity and if Homo faber is a construction species or an infrastructure species as some historians have put it. Linear features are what we construct: highways, railroads, power lines, fiberoptic cables, just look at our crop furrows. Beavers create what looks to us like chaos, there’s water ponding up everywhere with trees dying all over the place, and there’s sediment muckiness that smells a bit. This looks to us like fluid chaos, and I think we need to recognize that those kinds of beaver-modified or beaver-influenced systems are first the historical rule rather than the exception at the time of European arrival, but more important that those beaver systems are profoundly healthy as ecosystems compared to our infrastructure which are destructive to nature. We kill more than 1 million animals per day in the U.S. alone with our cars, whereas beavers create infrastructure that is highly beneficial to other animals from salmon and trout to waterfowl to moose and amphibians. It’s hard to name a species that doesn’t benefit from beavers at some point in its lifecycle.
STK: Beavers seem to have a human attitude to modifying the landscape. It reminds me of theories of terraforming other worlds. André Thevet described how on his way back to France from Brazil in 1556 most places hadn’t been colonized yet except how the island of Haiti was transformed by the Spanish into Hispaniola, “Little Spain,” in part by the influx of pigs they brought. So, this idea of terraforming in astrobiology seems pertinent here. You have a quote here, “We are a nation of floodplain dwellers and farmers, drawn to river valleys yet intolerant of riparian anarchy.” So, are we hostile to beavers because they challenge our sense of order?
BG: Right, the whole terraforming thing is funny because there was a story in, I believe Popular Science, in the 1930s that posited that beavers dug out the canals on Mars . So, that idea that beavers are world-makers have been applied to other planets as well. I think it’s instructive to think of the ways that beaver dams and human dams both impact the landscape, especially here in the West where I live. Every single river has a colossal mega dam on it, and those dams are immense, and they create enormous, consolidated reservoirs and they take a diverse and distributed approach to building ponds. Each of those ponds are only an acre or so, but they store more water in the landscape. You think about what the future of solar energy looks like, we’re on track to build giant industrial solar farms in the California desert when we could put a panel on every roof and opting for this more distributed and dispersed approach to power generation. That’s another interesting thing that beavers teach us: the value of the energy and strength of these distributed systems rather than the hyper-centralized systems that we tend to favor out of some misguided love of efficiency.
STK: Yeah, I just read this morning that our local NPR station was reporting that there’s a bill being proposed in the Missouri Assembly to ban water exportation from Missouri to the western states anticipating that Colorado, Utah, Arizona, et cetera are going to ask for our water eventually. It’s interesting to see that, we have the Missouri River here and the Mississippi River is on the eastern side of the state, and the Missouri floods at least once a year because they release the dams from the Dakotas that get all of the snowmelt and that floods down here typically. The Missouri is very heavily managed by the Army Corps of Engineers to the point that it’s faster than it used to be, but you know, it still floods.
BG: Look, the Missouri is one of the most hydrologically modified rivers in the U.S., and it’s certainly up there, and look at the catastrophic impacts it’s had most prominently on the Pallid sturgeon, and it speaks to the impact of human infrastructure being catastrophic for nature whereas beaver ponds are the world’s greatest fish production system. Trout and salmon grow exponentially faster in beaver ponds. The Missouri is like the Colorado River, one of those rivers that was incredibly full of sediment, “too thick to drink, too thin to plough,” so by damming the Missouri we changed water flows and sediment flows as well, and I think the beavers show us what a healthier and more beneficial relationship with sediment looks like. Beavers are capturing sediment as a resource which allows them to push more water onto the floodplain; they’re managing sediment better than we are in a lot of cases.
STK: Yeah, we actually saw one a couple of weeks ago on a Sunday morning crossing I-29 in Downtown Kansas City near the river, and it flopped itself over the barrier to get off the highway. I’m hoping there isn’t too much of a fall there, it’s all brush there. It was neat to see. We’re heavily redeveloping the riverfront now, so there’s going to be a lot more people up there were previously it was [among other things] an industrial waste dump by the railroads and such.
STK: I like what you said in the ninth chapter of this book when you were over in the U.K., and I’ve thought for a long time living here in Kansas City, my neighborhood was built here 100 years ago, and there weren’t trees here before they built this neighborhood, and all of the streets are named after colonial New Englanders. I’ve said then to people offhand that the developer tried to make this area a little New England, and as William Cronon wrote, New England was built out of the forests there as a new form of England. So, I wonder there, were you getting toward saying that we could look to Britain for the inspiration for American ecological policies, and secondly that the end goal of unlimited development would be how Britain is today?
BG: Yeah, to me one of the really striking things about visiting the U.K. for the book was how biologically improvised Britain and Ireland are today, and how fortunate we are to have the wildlife here in the U.S.: we have wolves, bison, and moose which were all species that once existed there that were annihilated there. And fortunately, here in the U.S. we were colonized recently enough, and we have enough rugged and inaccessible topography to allow these animals to be conserved, and we’ve done enough wildlife reintroductions here in a way that the U.K. is just beginning to get around to with beavers, and lynx someday. So, visiting made me feel extremely grateful for everything we’ve hung onto in the U.S., and beavers are one of those organisms of an animal in the Lower 48 that we pushed to the brink of extinction, but enough beavers survived up in Canada that we were able to use reintroduced beavers from Canada and some that hung on in Yellowstone National Park to reintroduce beavers on a wide-scale here in the U.S. Beavers today aren’t as ubiquitous as they were at their peak, not by a long shot so maybe we take them for granted a little bit and have beavers in the landscape.
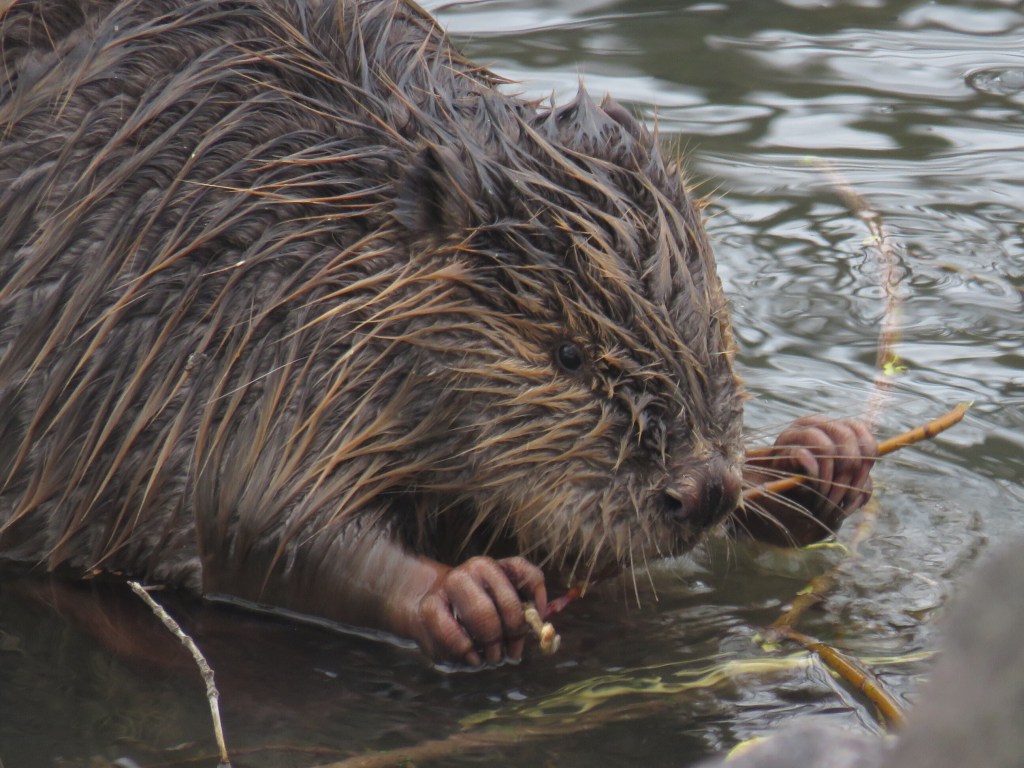
When I went back to England a year later on my book tour, I got to go on a nature walk where we saw beavers doing their thing and people were in tears with joy at seeing these beavers who had been eliminated from the landscape in the 1600s. It’s sort of like seeing the Loch Ness Monster, they’re these giant rodents with their paddle tails and they cut down trees with their teeth to build walls. They’re objectively these cool, bizarre, magical critters, and it was cool to be reminded of that in the U.K. where people are seeing this part of their natural heritage return to the landscape, while meanwhile they hang out in Downtown Kansas City, or Downtown Seattle, or in the Bronx River. It was a good reminder to appreciate our wildlife in general and beavers specifically.
STK: Yeah, I lived in London for a year doing my first Master’s, and you’d see some nature in the parks. I was fascinated looking at the webbing on some of the duck’s feet in St James’s Park where they’ve been protected because that’s been a part of the Palace for 300 years. But if you really wanted to see nature, you’d watch Naturewatch on BBC 1 on weekday mornings.
STK: So, has colonization forever changed beavers? Are they a different animal than they were 400 years ago?
BG: That’s a good question, and I think that ecologically and biologically they’re not. You could take a beaver from the 1300s and plop him down in modern North America and he’d do his thing and build dams and create ponds. They’ve survived so much over the last handful of centuries creating the kinds of landscapes you’d have seen before colonization. I went to Voyageurs National Park in Minnesota where these animals are protected from trapping and the landscape is conducive to beaver dam building, and there were dams that were 1000 ft long and 15 ft high, and I thought it was this great glimpse into pre-colonial America and what this would’ve looked like. These animals are the same but what’s changed is our relationship with beavers where before we perceived them as commodities that we extracted on an industrial scale to make hats. In the 20thcentury beavers began to be protected a little bit, and their populations began to increase, but all of a sudden, they were coming into conflict with humans and flooding our roads and cutting down our apple trees and flooding our irrigation ditches, and so we now see them less as commodities and more as pests. So, we still kill tens if not hundreds of thousands of beavers in the U.S. per year for causing conflict when we’re the nuisance species more than they are, they were here first. So, we need to transition out of the commodity phase and out of the pest phase and into the symbiotic phase where we harness all of the ecological benefits that these animals provide for us. Their ponds filter out water pollution and create oases against drought and prevent wildfires in some cases, especially in the West. They provide incredible fish & wildlife habitat and mitigate flooding in New England. Their value is immense beyond measure and we need to recognize that and treat them as ecological partners in conservation. Indigenous people in North America had that approach. The Blackfeet didn’t kill beavers but saw them as sacred because they created water holes to help other species. Respecting and honoring beavers isn’t new to western science, we just need to rediscover what native people knew for millennia.
STK: Are you working on any big projects now?
BG: I’m working on a book about fish, about fish as ecological engineers putting my beaver hat back on. Fish as drivers of human movement and culture over the course of our species’ own history and all the ways in which we lost fish from our lives and landscapes. I’ve always loved fish, both as quarry (I’m an angler) and as beautiful special specimens, like beavers they’re both concealed by the opacity of water.
BG: I look forward to coming back and joining you when that’s out in, I don’t know, 2056!
STK: Yeah, I’ve got a couple of books that I hope will come out before 2030 hopefully.
BG: Yeah, cool, I look forward to reading about three-toed sloths in human history.