On Toponymy – Wednesday Blog by Seán Thomas Kane
This week, the first in several scribblings about my research: how I connect historic places in my sources with their modern names.
When I started working on my dissertation and began downloading copies of André Thevet’s 1557 book Les Singularitez de la France Antarctique, I was struck by a curious question regarding the identity of some of the places which Thevet described along the disparate shores of the Atlantic Ocean in the middle of the sixteenth century. Some of these were readily accessible, the Portuguese fortress of Elmina for one remained an infamous outpost of the slave trade for centuries after Thevet’s 1555-1556 voyage. Likewise, Thevet made early references to regions like Florida, Mexico, Peru, and Brazil which are still known by those names today. I especially admire how he demonstrated the assimilative power of colonialization in the renaming of the Taíno island of Haiti into a newly christened European island literally called Little Spain, that is Hispaniola. Today, we know Haiti as the name of the western republic on the island of Hispaniola, and the Haitians as a people predominately of African descent, yet that term on its own originated with the indigenous inhabitants of that island and its neighbors.
This new world of names which Thevet hoisted upon the places he sought to describe in his Singularitez place that book in its historical context at the dawn of the European colonization of the broader Atlantic World and also in some cases provides a perspective on precolonial and early contact societies that have otherwise been diminished by the deluge of colonial toponyms which in many places replaced them. Thevet, like his fellow Frenchman Jacques Cartier, tended to use indigenous names for places, flora, and fauna. I’ve written in great detail about this concerning Thevet’s use of a French rendering of the Tupi name for the sloth, Haüt, and my dissertation includes similar analyses of the preservation of indigenous names for toucans, parrots, and macaws from Tupi for Thevet’s own French audience in his work. While his preference for indigenous names certainly added a lure of the exotic to his work, it is clear that he saw the utility of keeping these names and promulgating them to his readers.
When I am approaching a location in Thevet’s work I begin by seeing what the other editors and translators of Thevet down the last 468 years have done to familiarize what Thevet wrote for their audience. Thomas Hacket’s 1568 translation is beneficial to see how an Elizabethan reader might interpret distant Brazil and is useful for connecting Thevet’s Atlantic to Ralegh’s. Likewise, Giuseppe Horologgi’s 1562 translation is beneficial for understanding how Thevet was read by Italian humanists curious about the wider world; these readers were most likely thinking about Thevet’s stories in the context of the wider genre of travel literature typified in Italy by Giovanni Battista Ramusio’s (1485–1557) I Navigationi et Viaggi and for his natural history the collected works of Ulisse Aldrovandi (1522–1605). Moving from Thevet’s contemporaries, I then turn to a nineteenth century French reprint of the Singularites (as they were rendered in Modern French) edited by Paul Gaffarel. This edition was published in 1878 at a time when interest in Thevet and sixteenth-century French Brazil had a resurgence during the Third Republic which lasted into the early career of Claude Lévi-Strauss and Alfred Métraux, the two most prominent French anthropologists to consider the value of Thevet and his rival Jean de Léry as primary sources on early contact Tupinambá culture. Finally, I will turn to the two modern Brazilian translations of Thevet, Estêvão Pinto’s from 1944 and Eugenio Amado’s from 1978. Together these two sources are often my first choice when tracking down taxa of Brazilian flora and fauna and confirming Brazilian demonyms and toponyms. I figure these translators tended to have better access to Brazilian archives and scientific studies concerning their own country than their European counterparts considering the great distance between these continents. Lastly, several partial modern English translations of Thevet exist which provide their own regional analyses, most notable of these is Roger Schlesinger and Arthur Stabler’s 1986 translation of Thevet’s North American chapters which does particular justice to Thevet’s account of Canada.
The best sort of contributions any of us can make to collective human knowledge is built upon the conclusions and efforts of our colleagues past and present. The academy is a collaborative effort that only survives as long as we believe in the value of our work and of each other. I was reminded of this when I was in Boston during the Renaissance Society of America’s annual conference in March and felt such a potent sense of jubilation at that experience of camaraderie, I felt spending those four days among friends and colleagues. I especially see this among my fellow grad students and early career scholars who are the future of higher education and who are engaged in their work to a degree that in the span of a doctorate we readily become experts in our own disparate fields yet find solace and support in that common experience.
Returning to the task at hand, once I have consulted each of these various editions and translations of Thevet’s Singularitez, I then turn to his Cosmographie Universelle, a two volume magnum opus which was published in 1575. Volume 1 contains his accounts of Asia and Africa, and Volume 2 collected knowledge about Europe and the Americas. Thankfully, the Cosmographie Universelle has a good set of indices crafted by Thevet himself, which make navigating this gargantuan work easier. At this point, six years into my study of the man my PDF files of this book have enough of my own highlights & notes that I’ve added my own layer of internal navigation atop the cosmographer’s original efforts. Often, the Cosmographie Universelle supplements the Singularitez and adds greater depth and detail to it. For one, I first recognized Thevet’s claim that the sloth was an animal which could “live only on air” in the Cosmographie Universelle, only later noting the same claim in Chapter 52 of his Singularitez. In the Cosmographie Universelle it’s actually pulled out as a section heading in the margins of the book.
If again, Thevet either uses the same name for the geographical feature in question without any further context or the feature all together isn’t mentioned I will then turn to his 1586 Grande Insulaire, an unpublished manuscript of his which was edited by the preeminent French Thevet scholar Frank Lestringant and released in book form in 2016 by the Genevan publisher Droz. Lestringant has a long career studying Thevet, and his footnotes on the cosmographer remain among the best around. Often, he’ll be able to identify the places I’m looking for, but again his specialty is the history of French Protestantism in the sixteenth century, so toponymy isn’t necessarily his focus in reading Thevet.
This then leaves the last resort: a quick internet search to see what comes up when I type in Thevet’s sixteenth-century name for a given location. Often, I have better luck searching French or Portuguese Google than English Google (google.fr or google.pt) or even the French or Portuguese editions of Wikipedia, though all results from both the search engine and online encyclopedia need to be taken with a grain of salt and tremendous care. Anything I find online needs to be double-checked with other sixteenth-century sources, often Spanish in origin, to determine where Thevet got his name for the place from.
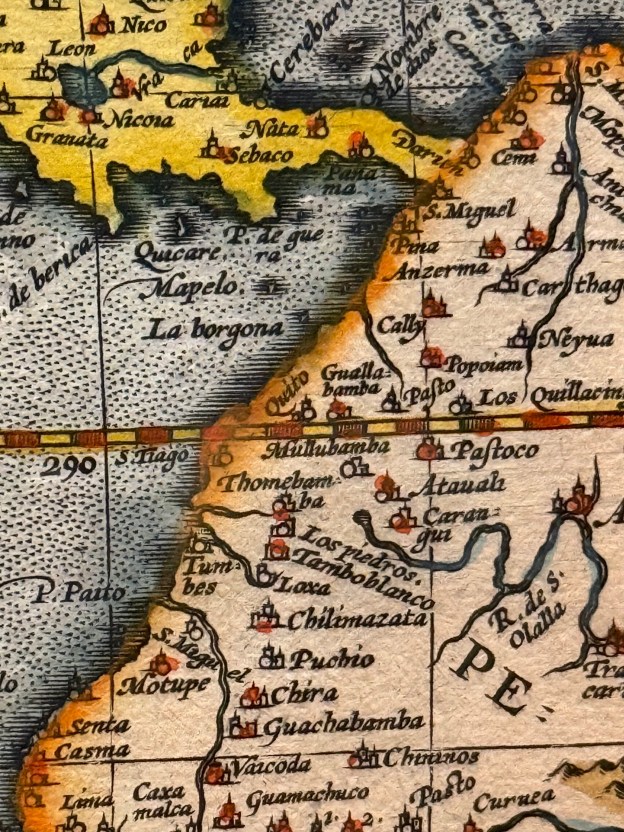
With my method in place, I want to put it to use explaining how I identified one particularly confusing toponym which Thevet used to describe a city on the coast of Peru. First, let me say that Thevet had a very broad understanding of Peru which included the entire side of South America west of the Andes, Panama, most of Central America, and the Caribbean archipelago beyond. Knowing this, I began by ignoring the word Peru and focusing instead on the coordinates Thevet ascribed to this city. He wrote in Volume 2, Book 22, Chapter 8 of his Cosmographie Universelle that this city was located “22 degrees from the Equator.”[1] Thevet used a Ptolemaic system for determining degrees of latitude, writing in the Singularitez that the Earth was divided into “360 degrees, and each degree is divided into 70 miles, which equals 16.5 leagues (96.48 km).”[2] By this calculation, the Earth’s circumference should be 34,732.8 km, which is 5,342.217 km short of the actual circumference at the Equator. This is a fitting comparison to make because the region where this city of “Saint Iacques” was located because it was certainly Equatorial in latitude considering he placed it among the cities of Quito & Ingapirca, which are located in modern Ecuador and Cusco & Cajamarca, which are located in modern Peru.
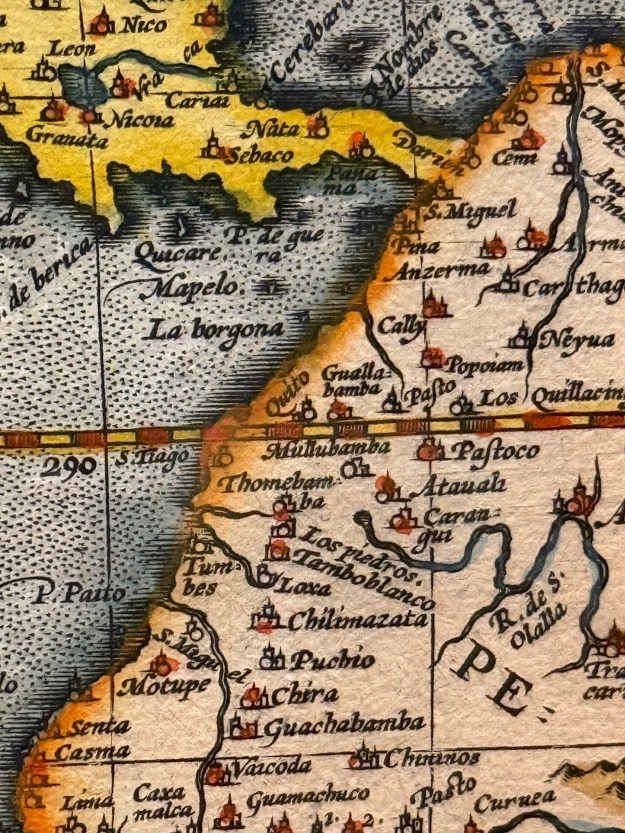
Generally, I found that Thevet’s degrees of latitude tend to be about double their modern equivalents, though this is a rough and often incorrect assessment. In this instance, that theory led me to search maps of the Peruvian coast around 11ºS looking for towns called Santiago, the Spanish translation of the Middle French Sainct Jacques. After spending a day searching, I gave up on this particular effort for the first time. Weeks later though, I returned to it after a conversation with frequent Wednesday Blog reader and one of my best friends Carmelita Bahamonde, who pointed out to me that her Ecuadorean hometown’s official, long name is Santiago de Guayaquil. I looked into it, and found several pages later hidden amid the text that Thevet had clarified further about this particular city of Sainct Jacques, writing that it was “the old port formerly named Guayaquil.”[3] I put this oversight at not finding this information where it was in that same source to my own poor eyesight, yet I remain grateful to my friend for confirming her hometown’s presence in Thevet’s Atlantic cosmography. He went into further detail about Guayaquil’s Spanish founder, the conquistador Francisco de Orellana (1511–1546) who led the first successful European expedition down the Amazon from the Andes to the Atlantic, losing almost all of his men along the way to desertion, disease, and attacks by the locals who knew to not welcome the Spaniards. In fact, when I began hearing about the lost Amazonian civilization first on PBS’s NOVA and later in one of my magazines, I believe it was in Smithsonian, I nearly leapt from my chair shouting “Thevet wrote about them!”

The value of André Thevet’s books lie in their character as sources for understanding the Americas just at the moment of these continents’ invention as the fourth part of a larger global world. The Singularitez and Cosmographie Universelle offer stories and perspectives of peoples and places that had not yet been subsumed into the colonial deluge that would submerge so much of the indigenous cultures of these continents in the coming centuries. This week, my colleague (and newly minted Ph.D.) Mary Katherine Newman at Oxford published a blog post with the History Workshop on restoring indigenous historical practices to equal prominence with the written European archive that we historians are trained to use. In many respects, Thevet did this, albeit through the perspective of a sense of civilizational hierarchy which was the accepted norm of his day. Métraux wrote that Thevet was the better of the sixteenth-century travelers to visit Brazil when it came to finding the precolonial and early contact Tupinambá in that same written archive. In my work, I’ve made a strong effort at acknowledging Tupinambá agency in their colonial encounters with the French, who were interested in trading with the locals rather than conquering, colonizing, or converting them. This allowed for a vibrant trading partnership to develop between the French and the Tupinambá which lasted through the mid 1560s. French colonial efforts might have taken off in Brazil had the colony, named France Antarctique, survived its first decade. Through a mix of sectarian infighting and increasing Portuguese dominance along the Brazilian coast, the French were expelled from France Antarctique by 1567. Still, one French toponym survives; the island where the French built their fort, which they named Fort Coligny, is today still known in Portuguese as Ilha da Villegagnon, after France Antarctique’s governor, Admiral Nicolas Durand de Villegaignon (1510–1571), the man who brought Thevet to Brazil to serve as the colony’s chaplain.
[1] Thevet, Cosmographie Universelle, vol. 2, 22.8, f. 970a.
[2] Thevet, Singularitez, f. 132v.
[3] Thevet, Cosmographie Universelle, vol. 2, 22.8, f. 972a.