On Systems of Knowing – Wednesday Blog by Seán Thomas Kane
This week, I argue that we must have some degree of artifice to organize our thoughts and recognize the things we see in our world.
Near the end of June on a Sunday afternoon visit to the Barnes & Noble location on the Plaza here in Kansas City when we were picking out books to gift to family, I espied a copy of Jason Roberts’s new paperback Every Living Thing: The Great and Deadly Race to Know All Life. In the Plutarchan model it is a twenty-first century Parallel Lives of Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon (1707–1788), two of the eighteenth century’s most prolific naturalists. I saved it as fun reading once I thought I’d done enough of my proper historical work. That moment came after I finished writing the first draft of the new introduction to my dissertation, a rather large addition to my doctoral study which is mostly historiographic in nature.[1] I’ve been reading Roberts’s book in my free time and delighting in the vibrant portraits he paints of the two men in question. I am a newer Fellow of the Linnean Society of London, elected in January 2025, and so I arrived to this particular book with a happy perspective on Linnaeus, whose Systema Naturae is cited in my dissertation as the first identification of the three-toed sloth by the genus Bradypus. At the same time, I’ve referenced Buffon’s Histoire Naturelle far more frequently in those moments when I’m following the legacy threads of my own Renaissance naturalists into the Enlightenment. After all, Buffon cited Thevet on several occasions where the savant referred to the same animals which the earlier cosmographer described two centuries before.
In spite of my own Linnean affiliation, and my use of Buffon’s corpus in the earliest stages of my broader historiography, I am still largely unfamiliar with these two men. I first knew of Buffon for his famous comments on his presumption of the diminutive nature of American animals when compared with their Afro-Eurasian counterparts, to which Thomas Jefferson retorted by sending Buffon evidence of an American moose.[2] I also know very little about Linnaeus, most of what I know of the Swede comes from lectures presented at the Linnean Society online including a recent lecture given in May by Staffan Müller-Wille, Professor in the History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences at Cambridge about Linnaeus’s Lapland diary from his northern expedition in 1732.[3] There is a new biography of Linnaeus by Gunnar Broberg titled The Man Who Organized Nature: The Life of Linnaeus which I have an eye on yet haven’t gotten a copy of quite yet. So, reading Roberts’s book is a quick introduction for me to this man who for me is most influential with his method of binominal taxonomy which has appeared time and again here in the Wednesday Blog. Yet this system followed after Linnaeus’s earlier alphabetical system for identifying plants by sexual characteristic. The basic premise here is that if there are 26 letters in the alphabet, we can then use that familiar framework to organize other complicated concepts for easy recognition. Linnaeus used this to categorize plants by their male and female sexual characteristics in his 1730 booklet Praeludia Sponsaliorum Plantarum, or Prelude to the Betrothal of Plants.[4] Therefore, Linnaeus could go around the botanical garden at the University of Uppsala in 1730 and quickly identify a plant as a J plant or a G plant. First reading this I thought of the way that letters are used by the Federal Reserve System to identify specific regional branches. Thus, J represents the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City and G the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago.
I like the idea behind Linnaeus’s alphabetic system yet having only 26 categories to describe the entire plant kingdom seems doomed to be flawed as it relies on a belief that all the plants that are known to exist are the ones that exist, that there’s nothing new under the Sun to be discovered. Roberts frames this in a biblical context, describing how Olof Celsius (1670–1756), one of Linneaus’s first professors, met the young Linnaeus when he was working on a project called the Hierobotanicum or Priestly Plants which was intended to be a compendium of all 126 plants mentioned in the Old and New Testaments.[5] Why would Linnaeus need more than 26 categories to contain all the plants known to the Ancients and to the Bible? Naturally, the flaws were apparent in this from the start by using a system of knowing which originated in the more arid landscape of the Levant rather than in the cooler and damper climate of Sweden. I’ve noticed this in my own life, how many cultural elements which we practice in the United States, notably the seasons, better fit the natural climate of New England and England proper than they do here in the Midwest with its far more variable conditions depending on the time of year, or even the given hour. Roberts deconstructed Linnaeus’s early efforts near the end of Part I of his book when he described Linnaeus’s first scholarly collision with Buffon after the Frenchman’s appointment by Louis XV to the position of Intendant of the Jardin des Plantes in Paris.[6] In a debate which Roberts calls “the Quarrel of the Universals” Linnaeus argued that species could be recognized from individual type specimens while Buffon countered that this ran the great risk of minimizing the diversity of life and eliminating potential variations in nature.
This got me thinking about systems of knowing, thus I decided to render the title of the original file for this blog post that you’re now reading (or listening to) De Systemarum Scientis in the full Latinate tradition of my own scholarship, or “On Systems of Knowing” in English. Why is it, for instance, that our Roman alphabet begins with A and ends with Z? The first half of that question is easier to answer: the Romans adapted our alphabet from the Greeks who started it off with α alpha, β beta, thus the noun alphabet itself. Yet the Greek alphabet ends with ω omega rather than ζ zeta, so why does ours end with Z? What I’ve heard about this is that the Greek letters that were adopted into the Roman alphabet were tacked onto the end of the line, or at least this is what I remember being taught when I learned to recite the alphabet in French in my undergraduate years. French calls the letter Y y-grec, or the Greek i. Likewise, everyone except for we Americans call the final letter of the Roman alphabet some variation of zed, which is a shortening of the Greek zeta. This better reflects that letter’s original sound in Greek, just as the cursive lowercase z is the lowercase Greek ζ just adopted straight into the Roman alphabet without any major changes.
So, when it comes to the organization of our knowledge there are things that we know in this same alphabetical order or in relation to this alphabetical order. Because the Roman alphabet is written left to right, we know that when it’s used to set up a coordinate system on a printed map that A will always appear to the top left, orientating the way the map should be held. Likewise, a reader can quickly scan through an index in any language written in the Roman alphabet by following along with the order of the letters. How individual languages index objects from that point on differs, but the foundational element remains the same. The Roman alphabet works best for Latin, the language for which it was originally developed, so it tends to be adapted in its phonetic values depending on which language is using it. This is why English uses the letter W to represent a [w] sound while German and in loanwords French uses W to represent a [ˈv] sound. Meanwhile, Irish represents the [w] and [ˈv] sounds with two digraphs, bh and mh that represent both depending on the context. Typically, bh represents [ˈv] while mh represents [w], but it depends on context. The reasoning behind this is that when the Roman alphabet was adapted by Latin speakers to fit Old Irish in the fifth and sixth centuries CE they approximated the phonology of their Latin in rendering the Roman alphabet usable for Irish. So, to these monks the Irish [ˈv] sound in a Gaelic name like Medbh sounded enough like how the letter b was used at the time that they used that letter to approximate this [ˈv] sound. It’s notable to me that in Modern Greek the letter β is today pronounced veta and in the Cyrillic alphabet the letter В represents this same [ˈv] sound while the letter Б represents the [b] sound that we English-speakers associate with the letter B. Cyrillic and its predecessor the Slavonic alphabet were being developed around the same time that the Roman alphabet began to be used for Irish so there must’ve been something going on with the pronunciation of people’s Bs becoming closer to Vs in late antiquity. Thus, the ways in which our alphabets represent specific sounds today reflect the prestige dialects of our two classical languages–Latin and Greek–as they were spoken over a millennium ago.
Consider then how we distinguish technical, scientific, or artistic terminology depending on the prestige language of that field. History has largely become a vernacular field, where we adapt terms that will be more familiar to the non-professional enough to initiate them into what Ada Palmer calls the History Lab. Yet often these terms will have etymologies beyond English itself. Consider the word photograph, or its more common shortened form photo. This word comes purely from Greek, the classical language more associated with science and technology. It blends the Greek φωτο-, the blending form of φῶς (phôs), or light with the suffix –γρᾰ́φος, from the verb γρᾰ́φω meaning to draw, sketch, or write. So, photography at its core is light writing. Neat! The word photography entered English from the French photographie, that etymology referring to the French origins of the art and craft of photography itself in the middle of the 1820s. Yet the linguists who modernized Irish a century ago decided to favor indigenous terminologies, rendering this word grianghraf using the Irish word grian for Sun instead of a variation of φωτο- (light) while adopting the Greek –γρᾰ́φος suffix to center this new Irish conception of the term within the same technological corpus as the English photograph. While consequential to have a particular Irish name for this technology that elevated the Irish use of photography as equal to any other culture’s photography and particular within the Irish language, it still remains rooted in the same western tradition of grounding our names for scientific and technical things in Greek.
Language directly influences how we know things because it is the vehicle by which we recognize those things around us. I know that a photograph is something made by “light writing” therefore I will also recognize that anything else beginning with “photo” also refers to “light” and that anything ending with “graph” refers to some form of record or writing. I come from a culture where light is connected with goodness and dark with ill. Likewise, for me I think of blue and green as happier colors rather than red or orange which are angrier colors. There is safety in light, in the daytime we can see people or things coming toward us easier than in the dark of night. At the Easter Vigil the celebrant lights the Paschal Flame which is then passed around the church so that we all share in the Light of Christ (Lux Christi) returned to the world with the Resurrection. The central question in my dissertation is linguistic: what did André Thevet (1516–1590) mean when he referred to the Americas overall as sauvage? This French word translates into English as both savage and wild, yet I chose to retain the original French to better represent the original concept which encompasses both concepts in English. This word was not necessarily racial in the modern sense, rather Thevet used sauvage to describe people, places, and things which existed beyond civilization. This word itself betrays its original meaning, that is city life. Thevet himself understood the sauvage to be the antonym of this city life. I describe it in the introduction to my dissertation in terms of light and dark, following the cultural connotations already illuminated: the city is the sun whence radiates the light of civilization. The further one goes from that sun, the darker things become and the less civilized they remain. Thevet’s sauvage existed at that furthest extreme in the dark. I imagine the character of Gollum in this sort of darkened existence, deep beneath the Misty Mountains uninterested in light save for the Ring of Power which consumed his day rendering it eternal night. In the literature of Thevet’s time a fine sauvage characterization is Caliban in Shakespeare’s Tempest, wild as the waters which wrecked King Alonso and his men on the island in Act 1 of that play.
Roberts notes how these linguistic attributes influenced Linnaeus’s systemization of humanity in the 1735 second edition of his Systema Naturae. The Swede divided humanity into four subcategories described by color over any other facet.[7] Roberts spends the following five pages questioning Linnaeus’s methodology, asking “why four?” and why these specific colors? There is some historical context for Linnaeus’s choice to refer to Black Africans, even Thevet referred to the varied peoples of Africa as “black” in his Singularitez de la France Antarctique. Thevet hints at a possible environmental cause for blackness, writing that the peoples “of Barbary” who are “the blackest” are “of the same manners and conditions as their region is hotter than others.”[8] Thevet’s understanding of African geography is somewhat uncertain, so his definition of Barbary may not align with the Berbers from whom the Barbary Coast of the Maghreb was named. Still, it hints at an understanding that the hotter, or more torrid, the climate got the darker the skin of the people would become. Roberts notes that the Portuguese were the first to use the “word negro to signify African origin or descent” in the middle of the sixteenth century.[9] This makes sense considering the Portuguese were the first European power to sail down the West African coast in the fifteenth century. That Roberts notes this Portuguese definition of blackness first appears in the middle of the sixteenth century likely refers to Damião de Góis’s (1502–1574) Chronica do Dom Emmanuel I of 1566 to 1567 which is an early source that I’ve consulted for information on the voyages of Vasco da Gama (d. 1524).[10] Geraldine Heng, the leading authority on medieval notions of race, wrote in her 2018 book The Invention of Race in the European Middle Ages that blackness was already well established as an element in religious and secular iconography by the beginning of the First Age of Exploration.[11] Roberts concludes his discussion of this particular racial element of Linnaeus’s great contribution to taxonomy sullenly noting that it’s thanks to Linnaeus that this cultural connotation of blackness with darkness was given scientific credence which continues to support racist ideologies to this day.[12]
How do we use our own words to describe things to which they are not suited, in turn transforming the nature of those things that they may become part of our own world? My research is most interested in understanding these questions of how those things at the boundaries of knowledge were understood by André Thevet using the tools afforded to him during the French Renaissance of the sixteenth century. Thevet used the word sauvage to do this and create a category of life against which he could measure and proclaim the existence of something civilized closer to home. Michael Wintroub, Professor Emeritus of Rhetoric at Cal-Berkeley, wrote in his 2006 book A Savage Mirror that Thevet’s countrymen sought to “civilize the barbarians” to make up for an insecurity they felt at being called barbarians themselves by Italian intellectuals at the turn of the sixteenth century during the French invasion of Italy under King Charles VIII (r. 1483–1498).[13] As long as there was someone else who the French could look down upon beyond their own cities they felt secure in their own civility. Yet the sauvage exists within a larger framework of singularities, a word which is central to Thevet’s cosmography. Thevet used the word singularity to describe those things which were exotic, wonderous, and immensely collectable in his eye and hopefully in the eyes of potential readers who would buy his books. I see various layers and categories of singularities in Thevet’s cosmography, for instance he only included images of certain animals in his book of the same name, the aforementioned Singularitez of 1557. The sloth and toucan were depicted as well as described, yet the mysterious Ascension Island aponar remained a bird worthy only of a textual description. This suggests that somethings were more singular than others, or more worthy of attention and the money needed to produce these woodcut images than others. These systems of knowing framed around the singularity are the subject about which I intend to write my first academic monograph. Classifying something as singular gives it an appeal which sets it aside from both the civil and the sauvage as belonging to a higher level of category which can include both the urbane and the agrestic.
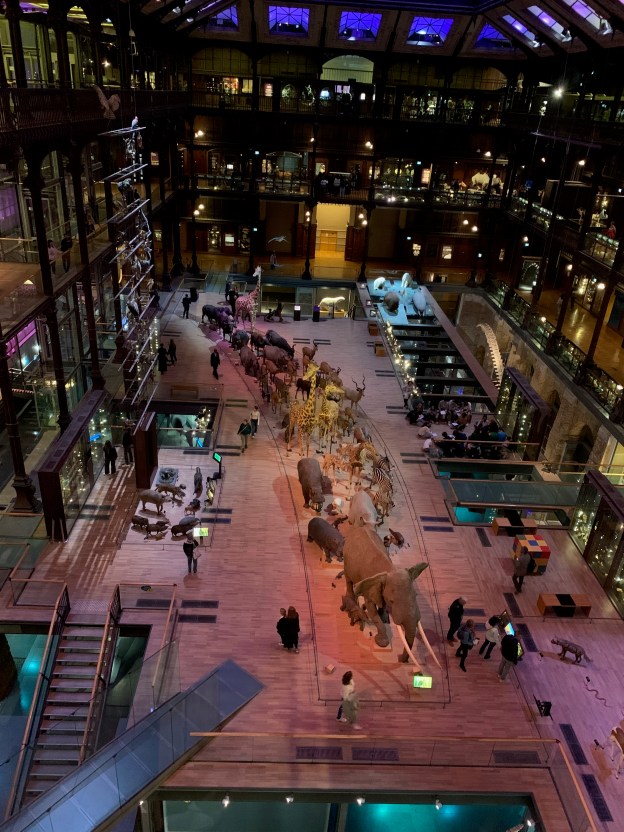
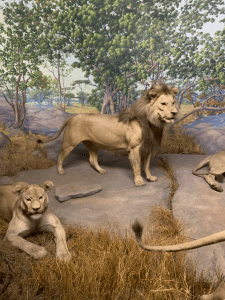
Jason Roberts describes Buffon and Linnaeus’s mutual missions to make something of themselves and to rise above their provincial origins to the heights of society. I laughed out loud reading Roberts’s introduction to Linnaeus’s character, what felt like an iconoclasm of sorts for this Fellow of the Linnean Society. “Carl Linnaeus was a Swedish doctor with a diploma-mill medical degree and a flair for self-promotion, who trumpeted that ‘nobody has been a greater botanist or zoologist’ while anonymously publishing rave reviews of his own work.”[14] Buffon by contrast took advantage of a golden opportunity to build his own demi-paradise at his manor in the Burgundy countryside until his good reputation as a botanist brought him to royal attention and the appointment as Intendent of Jardin du Roi.[15] The Jardin des Plantes, as Buffon’s charge is today known, is perhaps a better place to conclude than most. Situated in the Fifth Arrondissement across Boulevard de l’Hôpital and Rue Buffon from Gare d’Austerlitz, the Jardin is an urban oasis created for the purpose of crafting systems of knowing. Its original intent was to serve as a medicinal garden existing beyond the purview of the Sorbonne, Paris’s sole licensed teaching medical school in the seventeenth century.[16] I’ve spent several happy hours wandering through the Jardin, home to the Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle’s Grande Galerie de l’Évolution, the Galerie de Paléontologie et d’Anatomie compare, and the Ménagerie du Jardin des Plantes, which was home to Paris’s first resident giraffe whose story is delightfully told by Michael Allin in his 1998 book Zarafa: A Giraffe’s True Story, from Deep in Africa to the Heart of Paris.[17] While Allin’s heroine Zarafa is not today on display in the Grande Galerie de l’Évolution (she is instead today to be found in the Muséum d’Histoire naturelle de La Rochelle), the taxidermy in the Parade of African Mammals that is the centerpiece of the Grande Galerie represents a system of knowing animal life in itself.An elephant leads the parade followed by hippopotami, zebras, and giraffes with two such camelopards standing erect their long necks rising toward the upper galleries at the center of the procession. Behind them come the horned mammals, rhinoceroses, and at the rear a crouching lion watching its prey. This is a system that Buffon would have appreciated more than Linnaeus, one which represents the nature of individual beings more than species. Each stuffed specimen seems to have its own character, its own personality. They look about as one would expect they would in life. The great artifice of this is the idea of a parade itself, a very human notion indeed, and one that is infrequent enough to be nearly singular in character, a reason for a day out, worth putting in the social calendar of a city, town, or village no matter how large or small. A parade is its own system of knowing.
[1] For my recent essays referring to this current historiographic project see “On Sources,” Wednesday Blog 6.22, “On Writing,” Ibid., 6.27, and “On Knowledge,” Ibid., 6.29.
[2] Lee Alan Dugatkin, Mr. Jefferson and the Giant Moose, (University of Chicago Press, 2009).
[3] Staffan Müller-Wille, “Linnean Lens | Linnaeus’ Lapland Journey Diary (1732),“ moderated by Isabelle Charmantier, virtual lecture, 12 May 2025, by the Linnean Society of London, YouTube, 1:04:18, link here.
[4] Jason Roberts, Every Living Thing: The Great and Deadly Race to Know All Life, (Random House, 2024), 45–49.
[5] Roberts, 20.
[6] Roberts, 115–125.
[7] Roberts, 109.
[8] André Thevet, Les Singularitez de la France Antarctique, (Antwerp, 1558), 16r–16v. The translation is my own.
[9] Roberts, 109.
[10] Damião de Góis, Chronica do Felicissimo Rei Dom Emanuel, 4 vols., (Lisbon, 1566–1567).
[11] Geraldine Heng, The Invention of Race in the European Middle Ages, (Cambridge University Press, 2018), 190.
[12] Roberts, 110.
[13] Michael Wintroub, A Savage Mirror: Power, Identity, and Knowledge in Early Modern France, (Stanford University Press, 2006), 42.
[14] Roberts, xii.
[15] Roberts, 107.
[16] Roberts, 96–98.
[17] Michael Allin, Zarafa: A Giraffe’s True Story, from Deep in Africa to the Heart of Paris, (Delta, 1998).